Can high protein help conserve muscle mass and decrease fat mass during weight loss? And if so, what is the right amount that should be consumed? A recent paper published in 2013 discusses a study that looks into these very questions. The RDA is set at .8g per kg of body weight per day, the… Continue Reading
Category Archives: Macronutrients
More Protein Please.
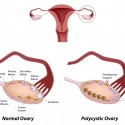
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder affecting nearly 6-8% of women within reproductive age. A recent study conducted by Sorensen et. al. evaluated the effects that a high protein (HP) diet compared to a high carbohydrate (HC) diet may have on overweight women suffering from PCOS. Past studies concerning PCOS and HP diets… Continue Reading

The Simple Truth about Simple Sugars – Comparing High Fructose Corn Syrup and Sucrose
A recent peer-reviewed article in the Nutrition Research Journal titled, “High-fructose corn syrup and sucrose have equivalent effects on energy-regulating hormones at normal human consumption levels,” authors Zhiping Yu, Joshua Lowndes, and James Rippe hypothesized that high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) and sucrose have essentially the same effect on human metabolism. 1 The results of… Continue Reading

Oil Pulling Over Mouthwash
Oil pulling is the practice of pulling, or swishing, oils (most commonly coconut, sesame, or sunflower oils) in the mouth. It may be a new way to use these oils that you haven’t ever thought of, but in reality this practice has been around for quite a while and is actually a common folk remedy.… Continue Reading

Is Just Eating Healthy Really Enough for PCOS?
For women diagnosed with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) obesity is a big issue. Losing weight and maintaining a healthy body weight is highly recommended because it helps reduce all other symptoms, one of which is high insulin resistance. Doctors have recommended a low glycemic (low-GI) diet (the recommended diet for diabetics) without a… Continue Reading

Olive Oil Benefits Still Superior Even When Heated in Cooking.
Olive oil is the main source of fat in Mediterranean regions and now is becoming very popular among other countries including United States, Argentina, Chile, Mexico, Australia and others. The popularity of this oil is mostly due to its nutritional benefits. Why is olive oil different from other vegetable oils? First of all, olive fruits… Continue Reading

How to Reduce Carcinogens in Your Steak
Cooking meat has several benefits: killing bacteria, making it easily digestible, improving texture, and probably most expected- improving flavor. But did you know compounds in your meat change during the heating process and become carcinogenic? The formation of carcinogens is a result of the reaction between creatine (muscle energy), free amino acids (building blocks of… Continue Reading

Power of Milk
We’ve talked about milk and its proteins before when we went over the different major kinds of proteins, but casein and whey aren’t milks only beneficial nutrients. The naturally high blend of protein and carbohydrates makes milk a great choice to fuel muscles after a workout so they are primed and ready to go again… Continue Reading

Saturated Fat May Be Safe for the Heart and Arteries
You probably have heard about the new popular diet, “Paleo diet”, revered by fans of crossfit and heavy weight lifting. In short, this diet is trying to simulate a cave man diet. Those people eliminate sugars and grains and substitute it with the more meat, eggs and fat in their meals. They also probably told… Continue Reading

What is in your chicken nuggets?
What is in you chicken nuggets? Don’t rush to answer, chicken. A recent study suggests that a favorite American fast food’s chicken nuggets contain less than 50 percent chicken. The University of Mississippi examined chicken nuggets from two national fast food chain restaurants in Jackson, Mississippi. Richard DeShazo and his colleges found that the nuggets… Continue Reading
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the dietary nutrients that supply energy, including fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Nutrients are substances needed for growth, metabolism, and for other body functions. Since “macro” means large, macronutrients are nutrients needed in large amounts.
Fats have four forms: saturated fats, monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats, and essential fatty acids. Carbohydrates contain both starches and sugars. Fat is found in meat, poultry, nuts, milk products, butter, margarine, oils, lard, fish, grain products, and salad dressings. Many people correlate fat intake with weight gain, but fats are essential for survival. We need fat for energy, growth, cushioning for organs, and maintaining cell membranes.
Carbohydrates are mainly found in starchy foods (e.g. grain and potatoes), milk, yogurt, and fruits. Other foods like vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds and cottage cheese contain carbohydrates, but in lesser amounts. Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of fuel and are easily used for energy in our bodies. Carbohydrates are also stored in the muscles for later use.
Protein is made up of amino acids. Protein is found in meats, poultry, fish, meat substitutes, cheese, milk, nuts, legumes, and in smaller quantities in starchy foods and vegetables. Protein is essential for growth, tissue repair, making hormones and enzymes, and immune function. Some amino acids are essential (meaning we need to obtain them from our diets) and others and nonessential (meaning the body can make them). Protein from animal sources contain all the essential amino acids we need. However, plant sources do not contain all the essential amino acids.







